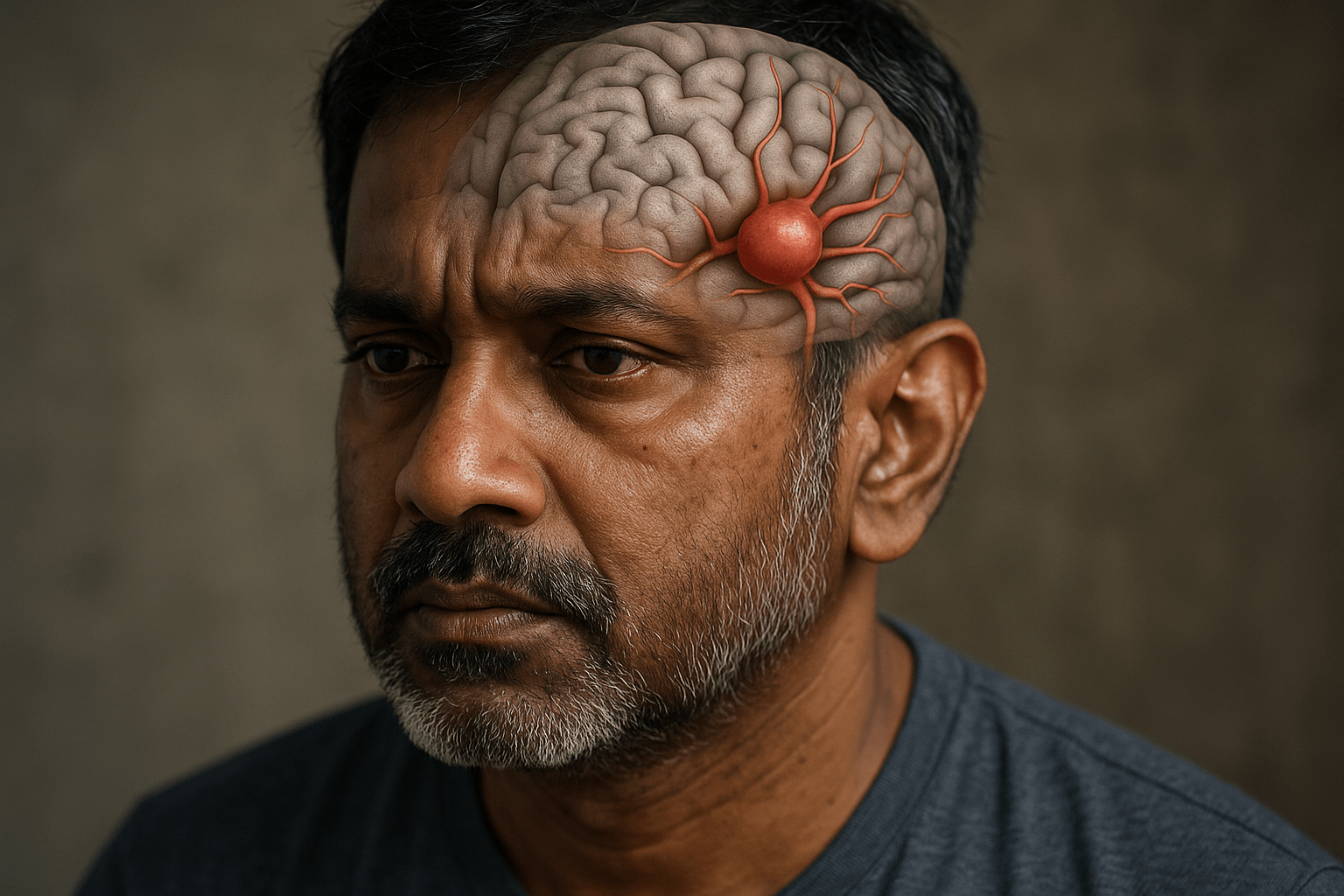
Brain aneurysms, also known as Cerebral Aneurysms, are silent but the most dangerous intracranial vascular disorders. They can rupture inside the brain, leading to haemorrhage. Early diagnosis, advanced neurovascular treatment in the form of clipping or coiling, and Neuro ICU care can significantly impact a patient’s outcome.
What Is a Cerebral Aneurysm?
A weakened or bulge area in the wall of a brain artery is called a Cerebral Aneurysm. This region may eventually balloon outward, creating a pouch-like structure. If it ruptures, it leads to bleeding in or around the brain, a subarachnoid hemorrhage, which is a medical emergency.
Warning Signs & Symptoms
Most unruptured cerebral aneurysms do not cause symptoms except for persistent headache and are often found on routine brain imaging. The following symptoms could be present in aneurysms that rupture:
- A person experiences a sudden, severe headache
Often referred to as the “worst headache of my life,” or “Thunder Clap Headache”. This condition requires immediate medical attention and may be a sign of a ruptured aneurysm. - Blurred or double vision
Vision impairment may result from the aneurysm’s pressure on nearby nerves supplying the eyes. - Drooping eyelid
Eyelid muscle control may be impacted by aneurysms close to the nerves that control the eye. - Neck pain or stiffness
Shows that the protective lining of the brain is irritated or bleeding. - Sensitivity to light (photophobia)
A common symptom is when bleeding affects the meninges (the brain lining). - Sensitivity to light (photophobia)
A common symptom is when bleeding affects the meninges (the brain lining). - Seizures
It may happen if the aneurysm disrupts the electrical activity of the brain. - Loss of consciousness
A possible outcome of elevated intracranial pressure and abrupt aneurysm rupture.
Get emergency neuro care right away if you or someone you know exhibits these symptoms – early treatment can save lives.
Why do Brain Aneurysms occur?
Understanding the risk factors behind cerebral aneurysms can help with prevention and early detection:
- Hypertension (high blood pressure)
Aneurysms are more likely when artery walls are weakened by continuous pressure. - Smoking
Accelerates the weakening of artery walls and damages blood vessels. - Family history of aneurysms
Particularly in first-degree relatives, genetic factors may increase the chances three times. - Head Trauma
It can harm the walls of the blood vessels, which may result in the development of aneurysms known as dissecting or Pseudoaneurysm.
- Specific Genetic Disorders
Blood vessel integrity can be weakened by conditions such as Ehlers-Danlos syndrome or polycystic kidney disease. - Age (More common after 40)
Over time, blood vessels naturally lose their elasticity, which raises the risk. - Gender (slightly more prevalent in women)
Vascular factors and variations in hormones might be involved.
Advanced Treatment Options Available in Delhi
Specialized care is essential after a cerebral aneurysm is diagnosed, whether it has ruptured or not. One of Delhi’s top Neurovascular Interventionists, Dr. Amit Aslam Khan, provides cutting-edge, minimally invasive procedures with the utmost safety and accuracy.
- Coiling (Endovascular Embolization)
A thin catheter is used to guide a soft platinum coil into the aneurysm. It blocks blood flow inside, causing it to clot and preventing the rupture.
The procedure is typically carried out under local anesthesia and is minimally invasive. - Balloon-Assisted Coiling
A tiny balloon is momentarily inflated during coiling to support the artery wall in an aneurysm with a broad neck. This helps in maintaining the coil’s position.
Used for complex Aneurysm Shapes or the wide neck of aneurysms. - Flow Diversion
Inside the artery across the aneurysm’s opening, a small stent is inserted. It allows the vessel wall to gradually heal by rerouting blood flow away from the aneurysms.
Best for the Giant or dissecting aneurysms. - Intra-saccular Flow Disruptors:
With the evolution in technology, devices are deployed within the aneurysm, preventing blood from entering the aneurysm. - Surgical Clipping (for selected cases)
Through open brain surgery, a tiny metal clip is inserted at the aneurysm’s neck to stop blood flow within it.
Often done if endovascular treatment isn’t suitable or a large blood clot is there in the brain, which needs to be removed.
Prevention & Lifestyle Tips
While not all causes are avoidable, adopting these protective habits can greatly reduce your risk:
- Control Blood Pressure:
Arteries are less stressed by routine monitoring and medication if it’s necessary. - Quit Smoking:
Giving up smoking reduces the risk and improves vascular health right away. - Eat a Heart-healthy diet:
Diets low in cholesterol and saturated fats support the maintenance of healthy blood vessels. - Manage Stress:
Blood pressure rises with prolonged stress. Yoga and meditation are examples of mindfulness exercises that can be beneficial. - Limit Alcohol Intake:
Drinking too much alcohol can harm the blood vessel walls and increase blood pressure. - Exercise regularly:
Strengthens your cardiovascular system, improves circulation, and helps control blood pressure.
Final Thoughts
If cerebral aneurysms are not identified and treated on time, they can be fatal. However, with the correct care, patients can live long, healthy lives. Don’t wait if you or a loved one is in danger. For professional assessment and cutting-edge treatment options, consult Dr. Amit Aslam Khan.
